
25 May 2021
India has reported Black Fungus (Mucormycosis) infections of epidemic proportions with more than 9000 reported recent cases and if the efficacy of India’s medical reporting system is true to form, the actual number could be many times greater.
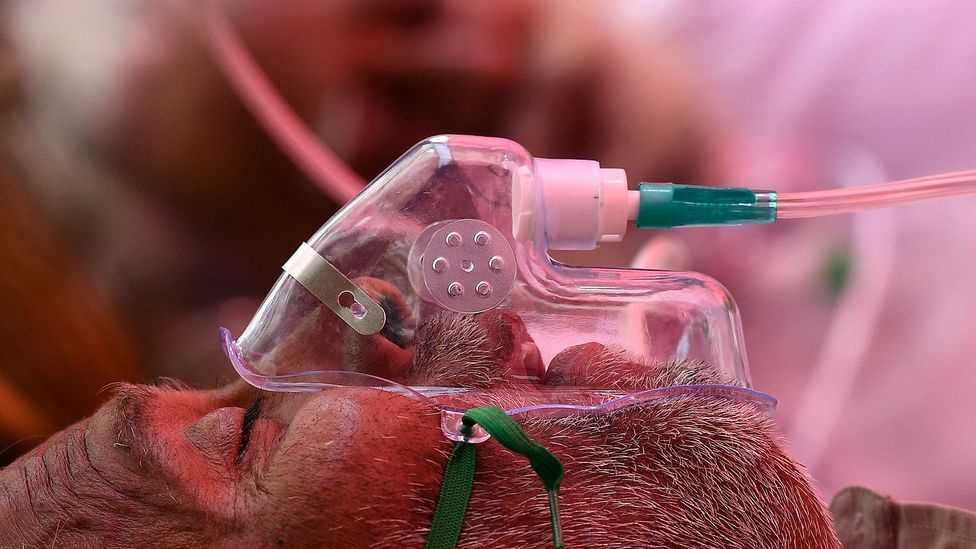
Powerful steroids can be used for the treatment of inflammation arising out of Covid-19 infection. One such corticosteroid is Dexamethasone which may be used to treat a range of autoimmune and inflammatory effects. To put this steroid into some perspective, it is six times stronger than Prednisone and twenty five times stronger than Hydrocortisone. One unfortunate side effect of such a Covid-19 treatment regime is serious suppression of the immune system leaving the patient more vulnerable to the likes of Black Fungus disease.
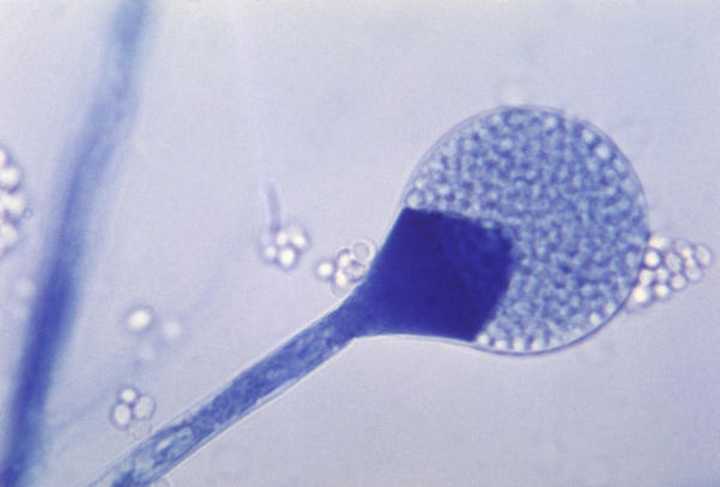
Several types of fungal moulds can give rise to Black Fungus disease. Such fungi aren't usually harmful to most people but can cause serious infections among those with weakened immune systems.
The disease is spread via airborne fungal spores and the five most affected states in India to date are Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, Rajasthan and Telangana.
Such infections are usually treated by antifungals, often administered intravenously and one of the most common medicines is Amphotericin B which is now in critically short supply in India.
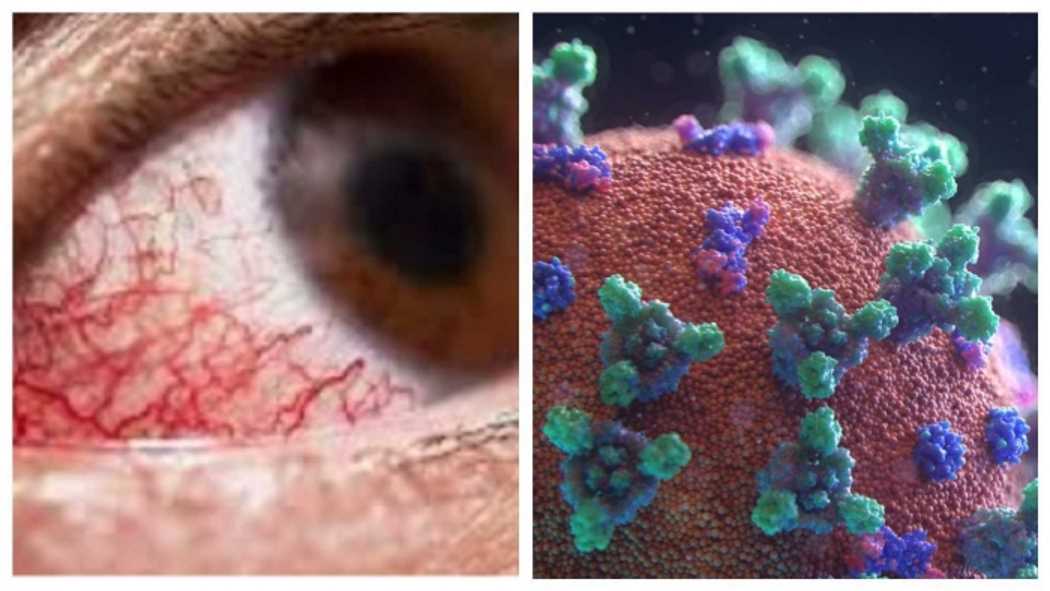
The disease begins to manifest as a skin infection in air pockets behind the forehead, nose and cheekbones and between the eyes and teeth. It can then spread to lungs and the brain. It leads to blackening or discolouration of the nose, blurred or double vision, chest pain, breathing difficulties and coughing of blood. Desperate medical treatment to save lives could include removal of eyes and jaws and patients being left with gaping head cavities. It compromises the circulation to distal organs and as a consequence produces what is known as necrosis or death of tissue which then becomes black, hence the description Black Fungus.
The disease is more prevalent in hot humid climates and can have a mortality rate as high as 54%.